Understanding How Butterfly Valves Are Combined in Modern Piping Systems
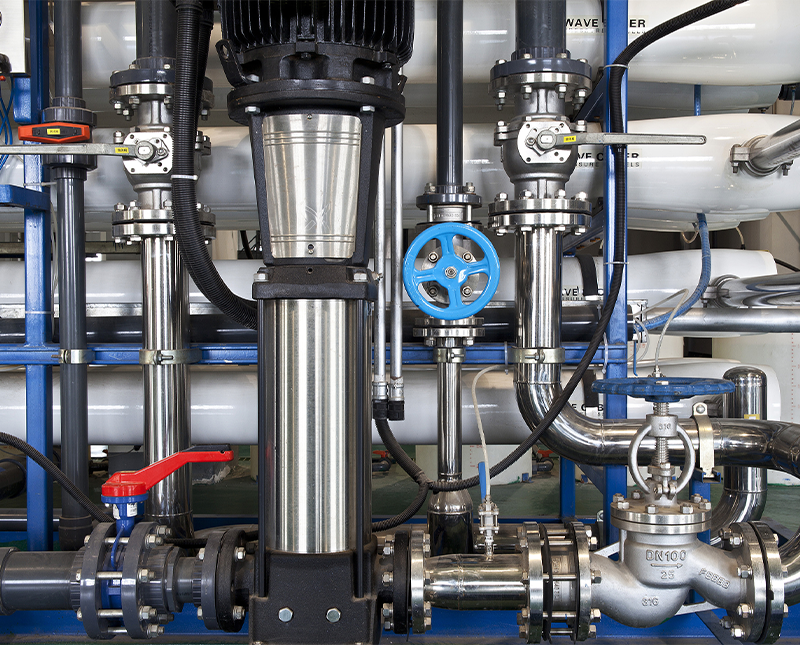
Combining butterfly valves are a practical engineering approach used to improve flow control, isolation safety, redundancy, and pressure management in industrial pipelines. Instead of relying on a single large valve, engineers often configure multiple butterfly valves in series or parallel to enhance reliability and optimize performance. This method is widely used in water treatment plants, HVAC systems, chemical processing, oil and gas transport, and power generation facilities.
Butterfly valves are favored due to their compact design, low cost, fast operation, and compatibility with automation. When properly combined, they can handle higher pressure ratings, provide better sealing performance, and allow staged flow control that improves system efficiency.
Common Configuration Methods for Combining Butterfly Valves
There are several proven ways to combine butterfly valves depending on the application requirements. Each configuration delivers specific performance benefits.
- Series installation for pressure control and redundancy
- Parallel installation for high flow capacity
- Isolation + control valve pairing
- Automated synchronized valve networks
Series Configuration for Safety and Pressure Staging
Installing two or more butterfly valves in series increases system protection by offering backup isolation. This setup is common in high-pressure pipelines where pressure drop must be controlled gradually. Each valve absorbs part of the load, reducing stress on seals and discs.
Parallel Configuration for High Flow Operations
Parallel butterfly valves allow higher flow volumes without oversized valves. Flow can be distributed evenly, reducing wear and improving response speed in large-scale fluid transport systems such as cooling water circulation.
Selecting Compatible Butterfly Valve Types for Combined Use
Not all butterfly valves perform equally when combined. Selecting the right valve design improves efficiency and longevity.
| Valve Type | Best Application | Advantages When Combined |
| Wafer Butterfly Valve | Tight spaces | Compact, cost-effective |
| Lug Butterfly Valve | Dead-end service | Independent isolation |
| Flanged Butterfly Valve | High pressure lines | Superior sealing strength |
| Triple Offset Valve | Extreme temperature | Zero leakage performance |
Material Compatibility and Sealing Performance
When combining butterfly valves, matching materials is critical. Disc materials such as stainless steel, ductile iron, or bronze must align with fluid chemistry. Elastomer seals including EPDM, NBR, and PTFE influence temperature resistance and leak prevention.
Improper material pairing can cause accelerated corrosion, seal swelling, and flow restriction. Industrial systems often use metal-seated butterfly valves when multiple valves are combined in high-temperature environments.
Pressure Rating and Flow Coefficient Considerations
Each butterfly valve has a pressure class rating and Cv (flow coefficient). When installed in series, pressure drops accumulate. Engineers must calculate total system resistance to avoid cavitation or reduced throughput.
- Check ANSI pressure class compatibility
- Verify combined flow capacity
- Prevent turbulence zones
Automation and Actuator Synchronization
Combining butterfly valves becomes more efficient with electric or pneumatic actuators. Synchronized opening sequences allow staged flow control and reduce water hammer effects. Smart valve positioners provide real-time monitoring for industrial automation systems.
In large processing plants, programmable logic controllers (PLC) manage multiple butterfly valves simultaneously, improving energy efficiency and operational safety.
Installation Best Practices for Combined Valve Systems
Proper alignment prevents disc binding and seal damage. Always maintain sufficient spacing between valves to minimize turbulence. Gasket selection must match pressure and temperature requirements.
- Ensure pipe flanges are concentric
- Use torque specifications correctly
- Test pressure before commissioning
Maintenance Strategies for Long-Term Performance
Routine inspection extends service life when butterfly valves operate together. Monitoring seat wear, actuator response time, and leakage ensures continuous reliability.
Predictive maintenance programs using vibration sensors and digital diagnostics are increasingly adopted in industrial valve networks.
Common Mistakes When Combining Butterfly Valves
Several design errors reduce system effectiveness:
- Mixing pressure classes
- Ignoring flow dynamics
- Improper actuator sizing
- Incorrect seal materials
Avoiding these issues ensures smooth operation and minimizes downtime across industrial valve systems.
Future Trends in Combined Butterfly Valve Systems
Advanced materials, smart automation, and digital monitoring continue transforming how butterfly valves are combined. High-performance coatings improve corrosion resistance, while AI-driven flow control optimizes energy use.
As industries demand higher efficiency and lower maintenance costs, integrated butterfly valve networks will remain a cornerstone of modern fluid control engineering.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch bahasa Indonesia
bahasa Indonesia