Introduction to Electric Ball Valves
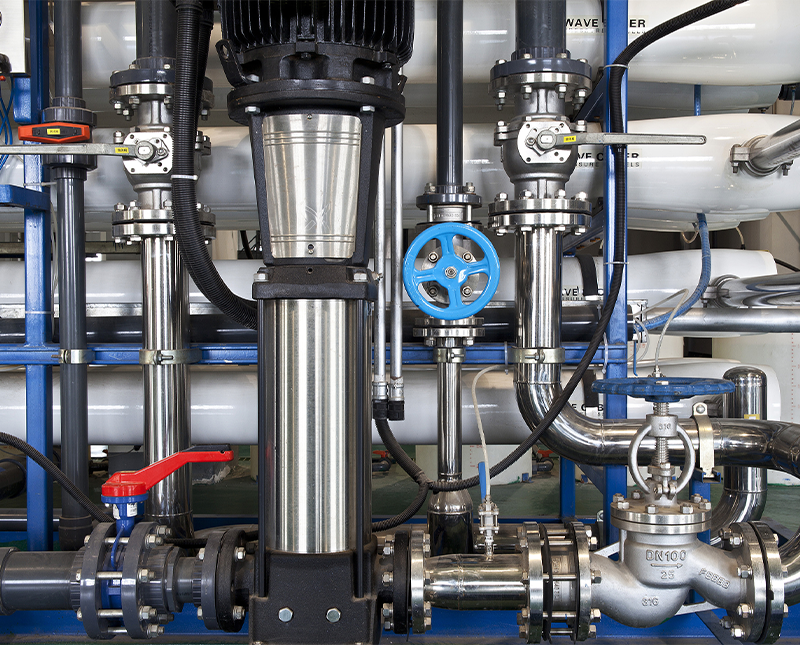
Electric ball valves are critical components in modern fluid control systems, allowing automated control of liquid or gas flow. Unlike manual valves, electric ball valves operate using an electric actuator, providing precise control and integration into automated systems. These valves are widely used in HVAC systems, water treatment plants, chemical processing, and industrial automation.
The primary advantage of electric ball valves lies in their reliability, durability, and ability to respond quickly to remote control signals. Understanding their construction, applications, and maintenance is essential for engineers, facility managers, and technicians aiming to optimize system performance.
Types of Electric Ball Valves
Electric ball valves come in various types depending on their structure, operation, and application. Selecting the right type ensures system efficiency and longevity.
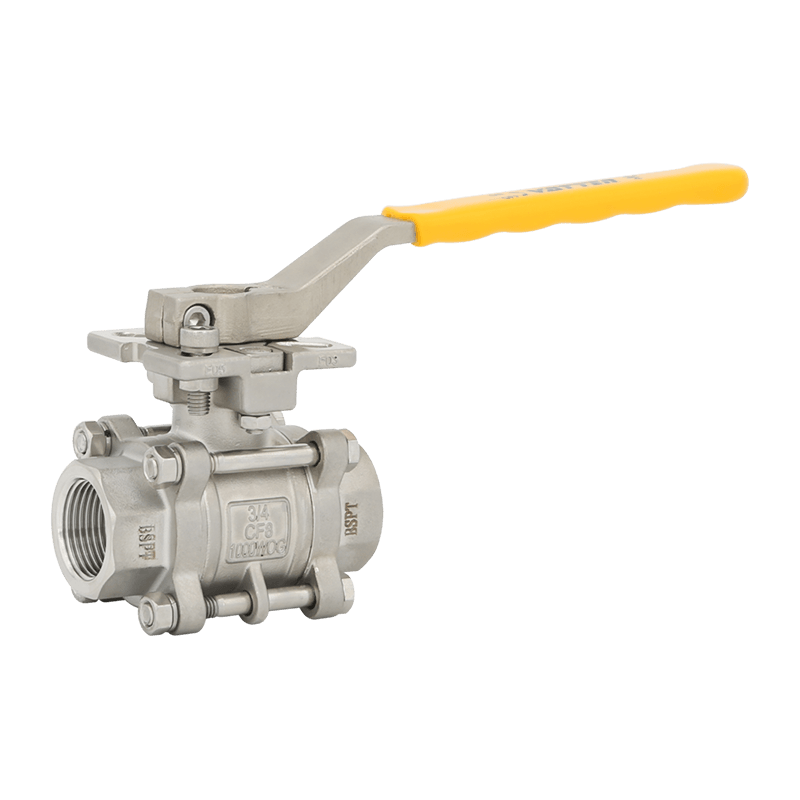
Two-Way Electric Ball Valves
Two-way electric ball valves are the most common type, featuring one inlet and one outlet. They provide simple open/close functions for fluid control and are widely used in residential and commercial HVAC systems, water distribution networks, and chemical lines.
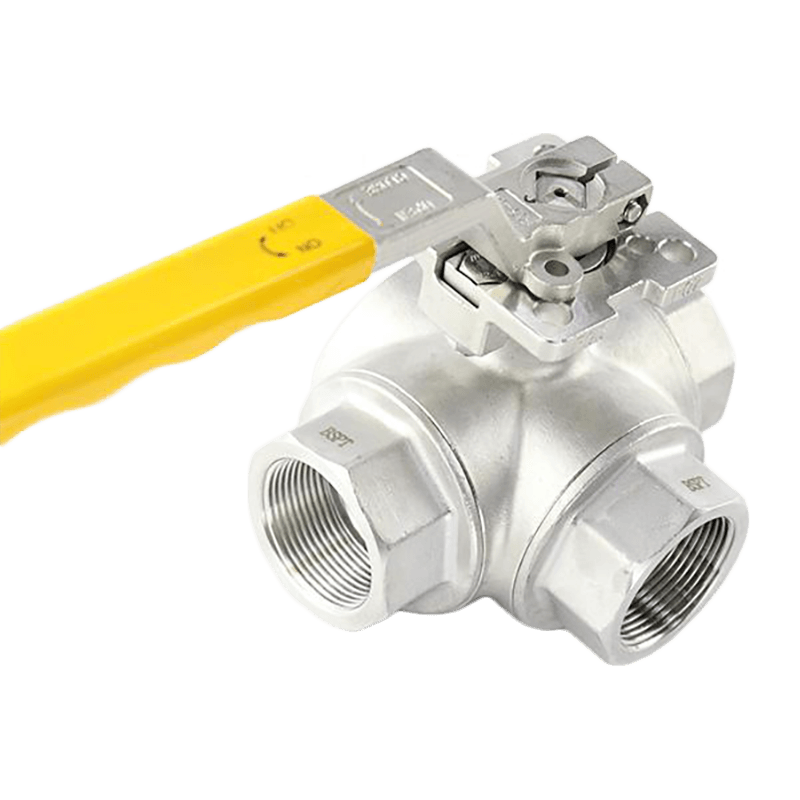
Three-Way Electric Ball Valves
Three-way electric ball valves have one inlet and two outlets or two inlets and one outlet, allowing fluid to be redirected between multiple pipelines. These valves are ideal for applications requiring mixing or diverting flows, such as in heating and cooling circuits, chemical processing, and industrial automation.
Multi-Turn Electric Ball Valves
Multi-turn electric ball valves allow precise modulation of flow rather than just on/off control. These valves are equipped with actuators capable of incremental rotation, making them suitable for applications where flow rates must be finely adjusted, such as laboratory processes and advanced industrial automation systems.
Key Components of Electric Ball Valves
Understanding the components of an electric ball valve helps with installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance. The main components include:
- Valve Body: Usually made of stainless steel, brass, or PVC, housing the ball and controlling fluid flow.
- Ball: A spherical element with a hole through the center that aligns with the flow path when open and blocks flow when closed.
- Seats: Sealing components ensuring a tight fit between the ball and valve body to prevent leaks.
- Stem: Connects the ball to the electric actuator for controlled rotation.
- Actuator: Electric motor that provides torque to turn the ball, can be modulating or simple on/off.
- Limit Switches: Indicate the valve’s position and ensure the actuator stops at fully open or closed positions.
- Control Wiring: Connects the actuator to controllers, PLCs, or remote switches.
Applications of Electric Ball Valves
Electric ball valves are widely used across industries due to their durability, automation capability, and precise control. Common applications include:
HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, electric ball valves regulate water or coolant flow to radiators, chillers, and boilers. They provide automated zone control, ensuring energy efficiency and consistent temperatures.
Water Treatment Plants
Electric ball valves are used to manage water flow, chemical dosing, and filtration processes. Their reliability under continuous operation makes them ideal for municipal and industrial water treatment facilities.
Industrial Automation
In manufacturing and process industries, electric ball valves are integrated into automated systems to control the flow of chemicals, gases, and liquids. Their precise operation allows for real-time adjustments and remote monitoring through SCADA or PLC systems.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation ensures long-term reliability and prevents premature failure. Key steps include:
- Check the valve specifications against system requirements, including pressure, temperature, and flow rate.
- Ensure correct orientation; most electric ball valves are installed with the actuator on top.
- Use appropriate sealing material (PTFE tape or gasket) to avoid leaks.
- Avoid over-tightening; excessive torque can damage the valve body or seats.
- Confirm that the actuator wiring matches the control system, verifying voltage and signal compatibility.
- Test the valve operation manually or via control system before commissioning.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of electric ball valves and ensures reliable operation. Maintenance practices include:
- Periodic inspection for leaks, corrosion, or wear on the ball, seats, and stem.
- Cleaning the valve internals if the system carries particulate-laden fluids.
- Lubricating the stem and actuator according to manufacturer recommendations.
- Checking actuator performance and limit switch calibration.
- Replacing worn seals, gaskets, or actuators as needed to maintain proper sealing and flow control.
Common troubleshooting issues include the valve failing to open or close, leaks, actuator noise, or inconsistent flow. These problems are usually caused by mechanical obstruction, misalignment, or electrical connection issues.
Performance Comparison Table
The following table compares key characteristics of different electric ball valve types to guide selection:
| Valve Type | Flow Control | Applications | Typical Materials |
| Two-Way | On/Off | Water, HVAC, Simple Automation | Brass, PVC, Stainless Steel |
| Three-Way | Diverting/Mixing | Heating/Cooling Circuits, Process Lines | Brass, Stainless Steel |
| Multi-Turn | Modulating | Precise Flow Control, Lab/Industrial Automation | Stainless Steel |
Conclusion
Electric ball valves are indispensable in modern fluid control systems due to their automation capability, durability, and precise control. Choosing the right type, installing correctly, and maintaining the valve regularly ensures reliable performance and reduces operational costs. By understanding the components, applications, and troubleshooting strategies, engineers and technicians can optimize system efficiency and longevity.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Indonesia
Indonesia