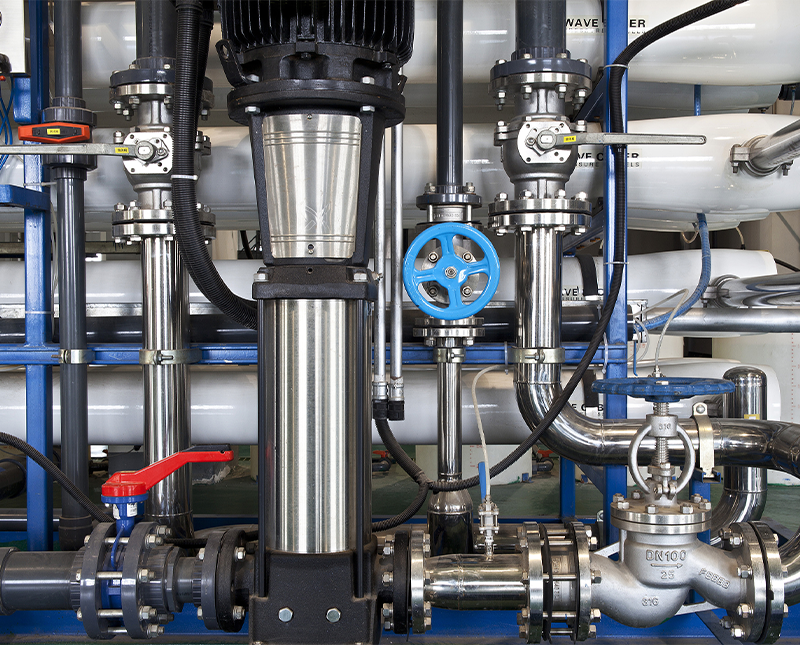
Flow regulation is a critical aspect of many industrial and commercial processes. From water treatment plants to chemical manufacturing, maintaining precise control over fluid flow ensures safety, efficiency, and product quality. Among the technologies available, Electric Flow Control Valves are widely used for their automation capabilities and responsive control. But how precise is their flow regulation, and what factors influence their performance?
Understanding Electric Flow Control Valves
Electric Flow Control Valves are devices that regulate the flow of liquids or gases in a piping system using electrical signals. Unlike manual valves, which require human intervention, these valves are connected to an actuator that adjusts the valve position based on a control signal, usually from a process controller or automation system.
The precision of flow regulation with these valves depends on several factors, including the valve type, actuator performance, control signal accuracy, and the characteristics of the fluid being controlled.
Key Factors Affecting Flow Regulation Precision
1. Valve Type and Design
The type of valve used can significantly impact regulation accuracy. Common types of Electric Flow Control Valves include:
- Globe valves: Known for fine control and precise throttling, globe valves are often chosen when accuracy is critical. Their design allows incremental adjustment of flow rates, making them suitable for processes requiring tight control.
- Ball valves: While ball valves are excellent for on/off control and high flow rates, their throttling capabilities are less precise than globe valves. However, certain engineered ball valves with specialized trims can improve regulation accuracy.
- Butterfly valves: Typically used for large-scale applications, butterfly valves are efficient but less precise in modulating flow. Their simplicity and compact size make them suitable where extreme precision is not required.
Valve selection should align with the required flow range, pressure conditions, and desired control accuracy.
2. Actuator Performance
The actuator is the component that physically moves the valve based on the electrical signal. The precision of flow control depends heavily on actuator characteristics, such as:
- Resolution: High-resolution actuators can make finer adjustments to valve position, improving flow regulation.
- Response time: Faster actuators can react quickly to changes in process conditions, reducing overshoot or lag.
- Feedback mechanisms: Many electric actuators include position feedback, which allows the control system to verify and correct valve positions, enhancing accuracy.
Choosing an actuator with appropriate resolution and speed for the application is essential for achieving precise flow control.
3. Control Signal Accuracy
Electric Flow Control Valves rely on control signals, typically 4–20 mA, 0–10 V, or digital protocols like Modbus or BACnet. The precision of flow regulation is influenced by:
- Signal resolution: Higher-resolution control signals allow for more precise adjustments.
- Signal stability: Fluctuations or noise in the control signal can lead to unintended valve movement, reducing flow accuracy.
- Control algorithm: The process controller’s algorithm (e.g., PID control) determines how effectively the valve responds to deviations from the target flow. Well-tuned control loops improve stability and precision.
4. Fluid Properties
The nature of the fluid being controlled also impacts flow regulation precision:
- Viscosity: Highly viscous fluids resist flow, potentially affecting valve response.
- Temperature fluctuations: Changes in temperature can alter fluid density, affecting flow rates if not accounted for in the control system.
- Pressure variations: Sudden pressure spikes can lead to overshoot or undershoot in flow, challenging precise regulation.
Understanding the fluid’s behavior is crucial when specifying and tuning Electric Flow Control Valves.
5. System Configuration
Flow precision is not solely determined by the valve itself. Piping layout, upstream and downstream conditions, and the presence of flow disturbances can influence performance:
- Turbulence: High turbulence can make flow less predictable, reducing control accuracy.
- Backpressure: Excessive backpressure can hinder valve movement or affect flow characteristics.
- Proper sizing: Oversized or undersized valves can compromise regulation, leading to instability or insufficient flow resolution.
A well-designed system with properly sized and located valves enhances overall control precision.
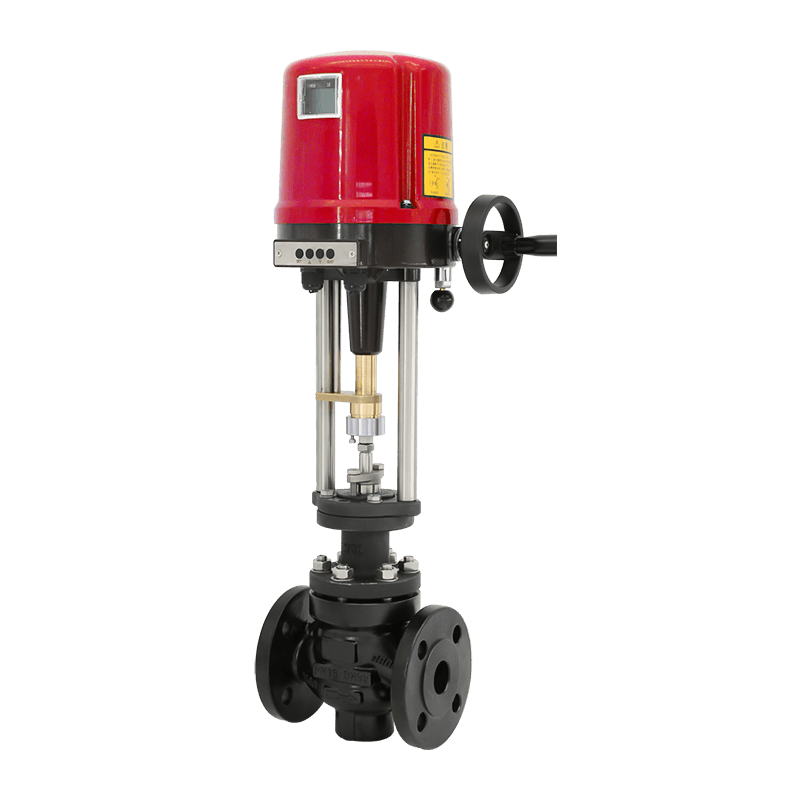

Measuring Flow Regulation Precision
Flow precision is typically evaluated using metrics such as:
- Flow deviation: The difference between the target flow and actual flow, usually expressed as a percentage.
- Linearity: The consistency of flow response relative to valve position. Ideally, valve movement should produce proportional changes in flow.
- Hysteresis: The difference in flow response when the valve is opening versus closing. Lower hysteresis indicates more precise control.
High-quality Electric Flow Control Valves, when properly installed and maintained, can achieve deviations as low as 1–2% of the target flow, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Practical Considerations for Improving Flow Precision
To maximize the precision of Electric Flow Control Valves, consider the following best practices:
- Regular maintenance: Periodic inspection and lubrication prevent sticking or wear that can reduce control accuracy.
- Calibration: Ensuring that the actuator and control system are correctly calibrated helps maintain precise flow regulation.
- System monitoring: Installing flow meters or sensors downstream allows real-time verification of actual flow versus setpoint.
- Valve selection: Match valve type and size to the application, considering the required range and flow resolution.
- Control tuning: Proper PID tuning or use of advanced control algorithms minimizes overshoot, oscillation, and steady-state error.
Applications Requiring High Flow Precision
Electric Flow Control Valves are often chosen for applications where precise flow regulation is critical, including:
- Chemical dosing: Accurate flow ensures consistent chemical reactions and product quality.
- HVAC systems: Precise control of chilled or hot water maintains comfortable and energy-efficient temperature regulation.
- Water treatment: Maintaining exact flow rates prevents over- or under-treatment, protecting water quality.
- Food and beverage production: Controlled flow rates are essential for consistent ingredient mixing and processing.
In these contexts, even small deviations can impact efficiency, safety, or product quality, highlighting the importance of precise valve operation.
Limitations of Electric Flow Control Valves
While Electric Flow Control Valves offer high precision, they are not without limitations:
- Cost: High-precision valves and actuators may be more expensive than manual or pneumatic alternatives.
- Electrical dependency: Power outages or signal failures can disrupt operation.
- Environmental constraints: Extreme temperatures, humidity, or corrosive environments may require specialized valves or protection.
Understanding these limitations helps ensure that the selected solution meets both performance and reliability requirements.
Conclusion
The precision of flow regulation with Electric Flow Control Valves depends on a combination of valve design, actuator performance, control signal quality, fluid characteristics, and system configuration. When properly specified, installed, and maintained, these valves can provide highly accurate flow control, making them indispensable in industries where precision is critical.
By carefully considering all influencing factors, monitoring performance, and maintaining the system, operators can achieve stable, consistent, and reliable flow regulation, improving efficiency, safety, and overall process quality.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Indonesia
Indonesia