Control valve vibration refers to the rapid opening and closing of the valve during operation, indicating that the control valve cannot stably maintain an appropriate position to sustain the predetermined proc...
READ MORE
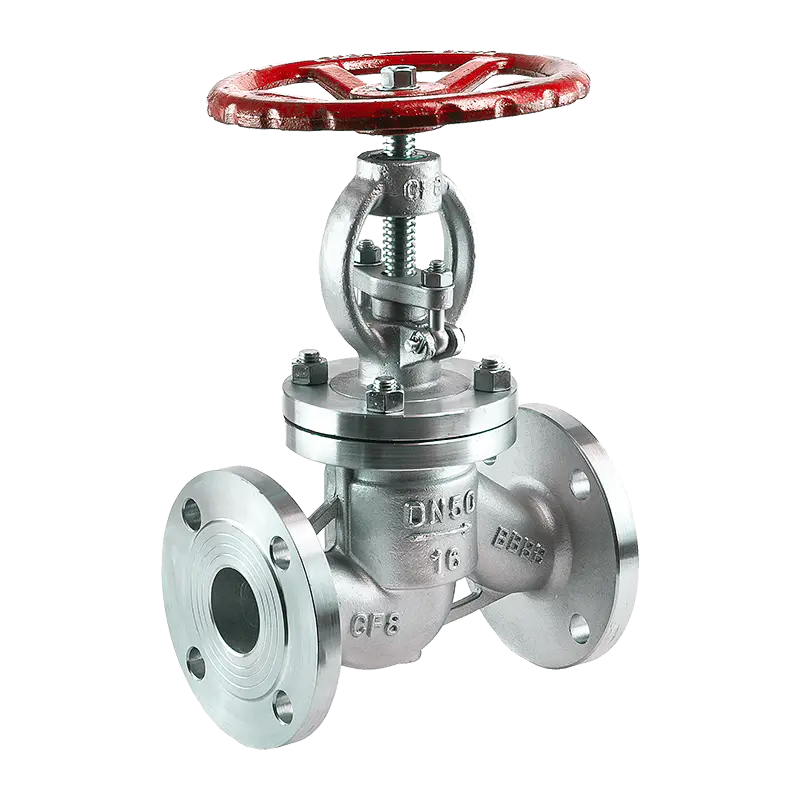
Manual Shut Off Valves Manufacturers
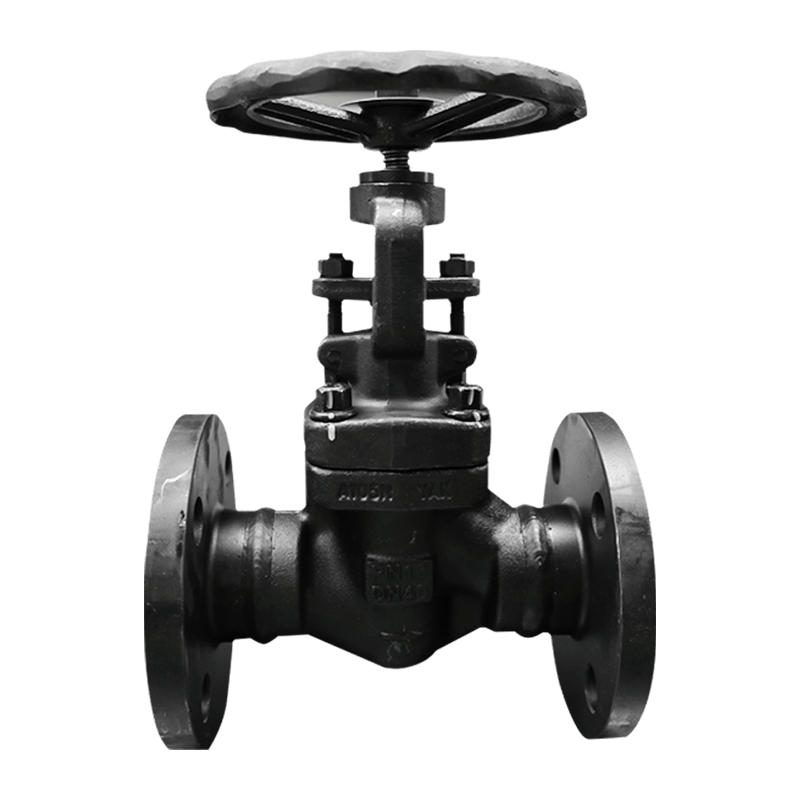
The VATTEN manual shut off valve is made of various stainless steel materials, ensuring excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance in different working environments. These materials are carefully selected to meet the demands of various industrial applications, such as high temperatures and harsh environments involving strong acids or bases.
The valve operates by a handwheel located at the top for opening and closing. This design provides stable operability and ensures that operators can easily adjust the valve even in challenging environments. The advantage of the handwheel drive system lies in its independence from external power sources, allowing valve control even in the absence of electricity.
Additionally, the design of the manual stop valve is specifically focused on temperature isolation, effectively preventing temperature differences from affecting the valve’s structure and performance. This ensures stable operation even under extreme temperature conditions, making the VATTEN manual stop valve particularly effective in applications requiring precise control and temperature stability
Vatten Valve Group, a globally renowned industrial automation valve enterprise originating from Saarland, Germany, specializes in the research, development, and manufacturing of core products such as automatic control ball valves, butterfly valves, and regulating valves. Leveraging our exceptional technological expertise, we deliver innovative valve solutions and professional technical support to critical industries including energy, chemical, water treatment, pharmaceutical, and food processing.
As Manual Shut Off Valves Manufacturers and Manual Shut Off Valves Company, the Group operates four state-of-the-art manufacturing bases strategically located in Shanghai, Tianjin, Lishui, and Jiaxing, China. To better serve international markets, we have established branch offices in key strategic locations including the United Kingdom, Turkey, Belarus, Saudi Arabia, and Indonesia. The establishment of our Indonesian office significantly enhances our service capabilities in the Southeast Asian market, ensuring timely and efficient technical support and services for local partners and clients.
Rooted in the German tradition of precision manufacturing, Vatten Valve maintains its focus on automatic control valves while strictly adhering to international quality standards. Provide Custom Manual Shut Off Valves. We are committed to continuous innovation, providing customers with superior performance products, professional technical support, and comprehensive fluid control solutions, empowering them to address complex industrial fluid control challenges.
-
-
Bottom discharge valves are flow-control devices installed at the lowest point of a vessel, tank, or hopper to allow controlled release of bulk solids, slurries, or liquids by gravity. They are a critical comp...
READ MORE -
Electric Flow Control Valves: Key Answer and Practical Value Electric flow control valves regulate fluid flow automatically using an electric actuator that adjusts valve position based on control signals. They...
READ MORE -
Key Conclusion: Why Check Valves Are Essential in Fluid Systems Check valves are installed to allow fluid to flow in only one direction and automatically prevent reverse flow without manual intervention. Their...
READ MORE
Key Factors Influencing the Durability of Manual Shut Off Valves
The durability of manual shut off valves depends largely on the material composition, sealing technology, and the working conditions under which they operate. Valves made from brass or stainless steel tend to have better corrosion resistance, while those made from carbon steel offer higher pressure tolerance. Regular maintenance such as cleaning the valve seat and lubricating the stem threads can significantly extend service life. Moreover, operating the valve within its rated temperature and pressure limits prevents premature wear of the internal components.
Operational Torque and Its Effect on Manual Shut Off Valves Performance
Operational torque refers to the amount of rotational force needed to open or close a valve. In manual shut off valves, excessive torque can indicate internal friction, scale buildup, or a misaligned stem. Conversely, very low torque could suggest worn-out seals or insufficient seating pressure. To maintain consistent performance, operators should measure and record torque values periodically, comparing them with baseline data to detect anomalies early and avoid unplanned downtime.
Application Environments That Challenge Manual Shut Off Valves
Certain environments pose greater challenges to manual shut off valves, particularly those with high humidity, corrosive vapors, or abrasive particulates. In marine or chemical industries, salt and chemical exposure can degrade valve surfaces and seals. To mitigate such effects, manufacturers often use PTFE-lined sealing materials, anodized coatings, or all-stainless-steel designs. Dusty environments may also cause particulate ingress into the stem mechanism, so protective caps or bellows seals are often used for long-term reliability.
Comparison of Common Handle Designs in Manual Shut Off Valves
The handle design of a manual shut off valve plays a crucial role in usability and control accuracy. Depending on application needs, various handle types provide distinct operational benefits. The table below compares common handle designs based on ergonomics, torque control, and maintenance requirements.
| Handle Type | Advantages | Limitations |
| Lever Handle | Quick operation and easy visual position indication | Requires space for rotation |
| Handwheel | Precise control over flow adjustment | Slower to operate; larger footprint |
| T-Handle | Compact design for tight spaces | Limited torque leverage |
Maintenance Practices to Prevent Leakage in Manual Shut Off Valves
Leakage is one of the most common issues in manual shut off valves, often caused by worn packing or misaligned seating surfaces. To prevent leakage, maintenance personnel should conduct visual inspections for signs of corrosion or residue buildup and replace gaskets as needed. Lubricating moving parts helps reduce wear on the valve stem, while tightening the packing gland evenly ensures a uniform seal. Avoid overtightening, as it can deform the packing and lead to future leaks.
- Use appropriate sealing materials compatible with the fluid type.
- Inspect packing gland compression during each maintenance cycle.
- Clean the sealing surface before reassembly to maintain integrity.
- Check for stem corrosion that can cause micro-leakage.
Manual Shut Off Valves in Safety Systems
Manual shut off valves are often integrated into safety systems to isolate specific sections of a process line during emergencies or maintenance. Their reliability is crucial in preventing backflow or uncontrolled release of hazardous fluids. For critical operations, valves with locking devices or position indicators are preferred, ensuring operators can verify valve status quickly. Some facilities employ double block and bleed configurations to enhance isolation and safety assurance.
Selecting the Right Seal Material for Manual Shut Off Valves
Seal material selection determines how well a manual shut off valve performs under specific process conditions. Different media—such as oil, steam, or acids—require compatible sealing elements to ensure long-term stability. For example, PTFE seals are suitable for most chemicals due to their excellent chemical inertness, while graphite seals are used for high-temperature applications. EPDM and NBR are common in water and gas systems, balancing flexibility and sealing strength.
| Seal Material | Typical Application | Temperature Range (°C) |
| PTFE | Chemical, pharmaceutical, food industry | -50 to 200 |
| Graphite | High-temperature steam and oil | -200 to 450 |
| EPDM | Water, gas, low-pressure air | -40 to 150 |
Human Factors in Manual Valve Operation
Human factors such as ergonomics, visibility, and accessibility play a significant role in the safe and efficient use of manual shut off valves. Operators should not have to exert excessive force or work in awkward positions to reach or operate a valve. Color-coded handles or position indicators can reduce human error, especially in complex piping networks. In safety-critical installations, clear labeling and routine operator training further reduce the likelihood of incorrect operation or delayed response during emergencies.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Indonesia
Indonesia